China's Carbon Emissions Decline in H1 2025: A Comparative Analysis with U.S. Emissions and Global Climate Implications
China’s carbon emissions dropped 1% in the first half of 2025 due to renewable energy growth. Comparative analysis with U.S. emissions highlights global climate implications.
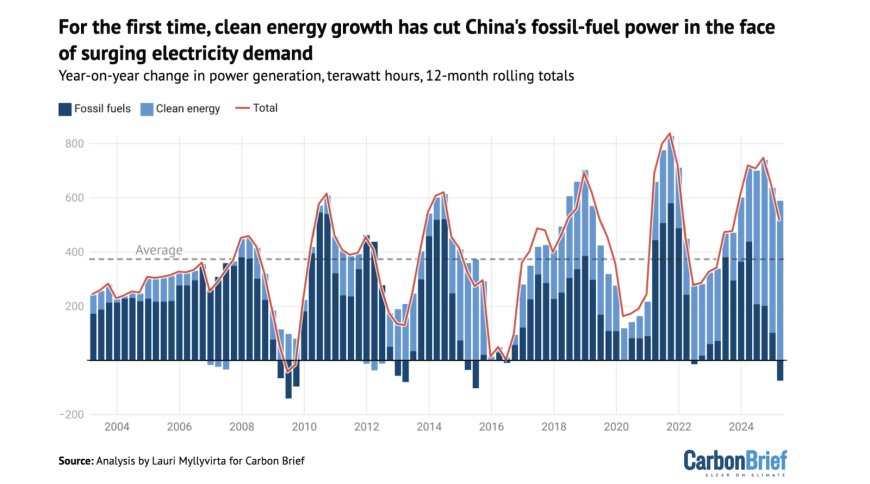
In a significant development for global climate policy, China has reported a 1% reduction in its carbon dioxide emissions during the first half of 2025 compared to the same period in the previous year. This decline is attributed to an increased reliance on renewable energy sources for electricity generation. However, the overall emissions trajectory remains influenced by ongoing industrial activities and energy consumption patterns.Reuters+2Reuters+2
China's Emission Reduction: Key Drivers
-
Renewable Energy Integration
The Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA) highlights that China's power sector emissions fell by 3% in the first half of 2025. This reduction is primarily due to a surge in renewable energy capacity, including solar and wind power, which has contributed to a record low carbon intensity of electricity generation. Data from electricitymaps.com indicates that the carbon intensity per kilowatt-hour of electricity averaged 492 grams during this period, marking a significant improvement.
-
Coal-to-Chemicals Sector: A Contradictory Trend
Despite advancements in renewable energy, the chemicals industry in China has experienced a 20% increase in coal usage for synthetic fuels and petrochemical products. This sector's emissions have risen by 3% since 2020 and are projected to increase by an additional 2% by 2029, posing challenges to the nation's decarbonization goals.
Comparative Analysis: China vs. United States
While China has made strides in reducing its emissions, the United States has faced challenges in curbing its carbon output. In the first five months of 2025, U.S. power sector emissions rose by 5% to approximately 640 million metric tons, primarily due to increased coal usage. This uptick is attributed to higher natural gas prices, which led utilities to favor coal-fired power generation. Conversely, China's commitment to renewable energy has resulted in a decline in its emissions, underscoring the impact of energy policy on emission trajectories.Reuters
Global Climate Implications
The emission trends in China and the United States have significant implications for global climate efforts. China's reduction in emissions contributes positively to international climate goals, while the U.S.'s increased emissions highlight the challenges of balancing energy demands with environmental considerations. These developments underscore the need for comprehensive and consistent climate policies across major economies to achieve meaningful progress in combating climate change.
Conclusion
China's 1% reduction in carbon emissions in the first half of 2025 reflects positive strides towards its climate objectives. However, challenges remain, particularly in sectors like coal-to-chemicals. The comparative analysis with U.S. emissions trends emphasizes the importance of sustained and coordinated efforts in renewable energy adoption and emission reduction strategies to meet global climate targets.Reuters+1














